Segmentation of Tricuspid Valve Leaflets From Transthoracic 3D Echocardiograms of Children With Hypoplastic Left Heart Syndrome Using Deep Learning
Introduction/ Abstract
Hypoplastic Left Heart Syndrome (HLHS)
HLHS occurs when only the right ventricle and tricuspid valve (TV) support circulation.
-
TV → Tricuspid Valve
-
3DE → 3D Echocardiography
-
TEE → Transesophageal Echocardiography
-
Used an FCN to segment TVs from transthoracic 3DE
-
Dataset split: 133 3DE scans for training, 28 for validation
-
Metrics used: Dice Similarity Coefficient (DSC) and Mean Boundary Distance (MBD)
-
Results:
- Annular curve
- DSC (median): 0.86
- MBD (median): 0.35
- Merged
- DSC (average): 0.77
- MBD (median): 0.66
- Annular curve
Anatomical details:
- Annulus: the fibrous ring that serves as the base structure for the valves
- Leaflets: the thin flaps that open and close with each heartbeat — think of these as hinges and doors
Repairing the TV is difficult due to its complex geometry.
Limitations
- 2DE: requires mental reconstruction by the clinician
- 3DE: pediatric transthoracic scans are of lower quality compared to adults
- TEE: affected by artifacts and limited cooperation in children
Dataset Details
Basic Information
- 161 TEE 3DE images from 239 unique HLHS patients
- 133 for training (pre-stage 1: 24; post-stage 1: 21; post-stage 2: 12; post-stage 3: 76)
- 28 for validation/testing
Ground Truth Creation
- Annular curve is marked
- TV leaflets are segmented
- Valve quadrant landmarks corresponding to APSL (Anterior, Posterior, Septal, Lateral) regions of the annulus are identified
- Commissures (boundaries between the leaflets and annulus) are marked: ASC, PSC, APC
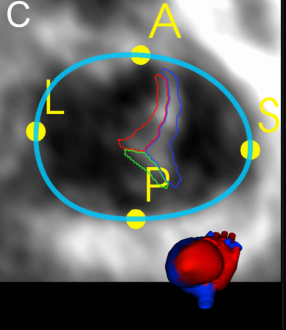
The Annular Curve with quadrant landmarks
Model Architecture
- Base architecture: VNet
- Modifications:
- Changed activation from PReLU to ReLU based on experimental feedback
- Changed convolution filter sizes from 5×5×5 to 3×3×3
Experiments and Methodology
The paper explores different input configurations for segmentation, including:
- Types of input frames
- Inclusion of the annular curve
- Inclusion of commissural landmarks
- Resampling
All combinations of these modifications were tested across the different frame types, yielding 32 experiments in total (4 input frame types × 8 variations).
Input Frames
- Single-Phase: only the targeted mid-systolic (MS) frame
- Two-Phase: adds the mid-diastolic (MD) frame in addition to MS; provides information on valve opening
- Four-Phase: includes end-systolic (ES) and end-diastolic (ED) frames, resulting in 4 frames (ES, ED, MS, MD)
- Consecutive Systolic Phases (CSP): includes 10 frames around MS (5 before, 5 after), providing temporal context
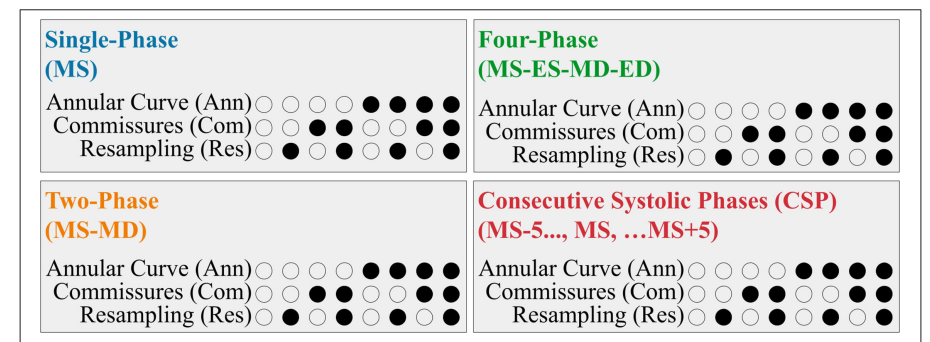
Results
The best performance was achieved when using CSP frames with annular curve, commissural landmarks, and resampling — i.e., the maximum information available. This configuration outperformed human annotators.
- Individual leaflets: DSC = 0.81, MBD = 0.38 mm
- Merged valve: DSC = 0.85, MBD = 0.33 mm
Paper Breakdown
Category:
Clinical application research applying FCNs to segment tricuspid valve leaflets from 3D echocardiography in pediatric patients with congenital heart disease.
Context:
Addresses a critical need in pediatric cardiology where manual segmentation of tricuspid valves in HLHS patients is extremely time-consuming (2–4 hours) and highly variable between operators. While prior work focused on atlas-based approaches, this represents the first application of deep learning to pediatric congenital valve segmentation.
Correctness:
The methodology is sound with appropriate validation. However, the training dataset is imbalanced across surgical stages (58% post-stage 3 vs only 9% post-stage 2), which may affect generalizability.
Contributions:
- First deep learning approach for tricuspid valve segmentation in congenital heart disease
- Systematic evaluation of different input configurations (frame types, landmarks, preprocessing)
- Segmentation accuracy comparable to human intra-observer variability
Clarity:
The paper is well-structured, with clear methodology and comprehensive results. The clinical context is well-explained for a technical audience, though the 32 experimental configurations make the results section dense.
Additional Notes:
- Your observation about MBD being relevant for VR-Heart shell creation is insightful — boundary accuracy is indeed critical for haptic and simulation applications.
- The issue of signal dropout (where FCNs create holes that humans fill using anatomical knowledge) is a common challenge in medical AI and worth considering for cardiac applications.
- While the experimental design is strong, dataset limitations and class imbalance suggest cautious interpretation, particularly for underrepresented surgical stages.
Follow-up considerations:
- Use of MBD in VR-Heart applications
- Wilcoxon signed-rank test for pairwise statistical comparison
- Shapiro-Wilk test for normality